Using Runtime Variables
Runtime Variables can be accessed via the**kwargs parameter in your block
function.
- integer
- string
- float
- boolean
- list
- dictionary
- set
Creating Runtime Variables
In Mage editor
You can create new global variables from the Mage UI through the “Variables” tab in the sidekick. Click the “New” button, and configure your variable’s name and value, and press Enter to save. To edit global variables, hover over the variable and click on the edit button. You can edit the variable name and/or value, and press Enter to save.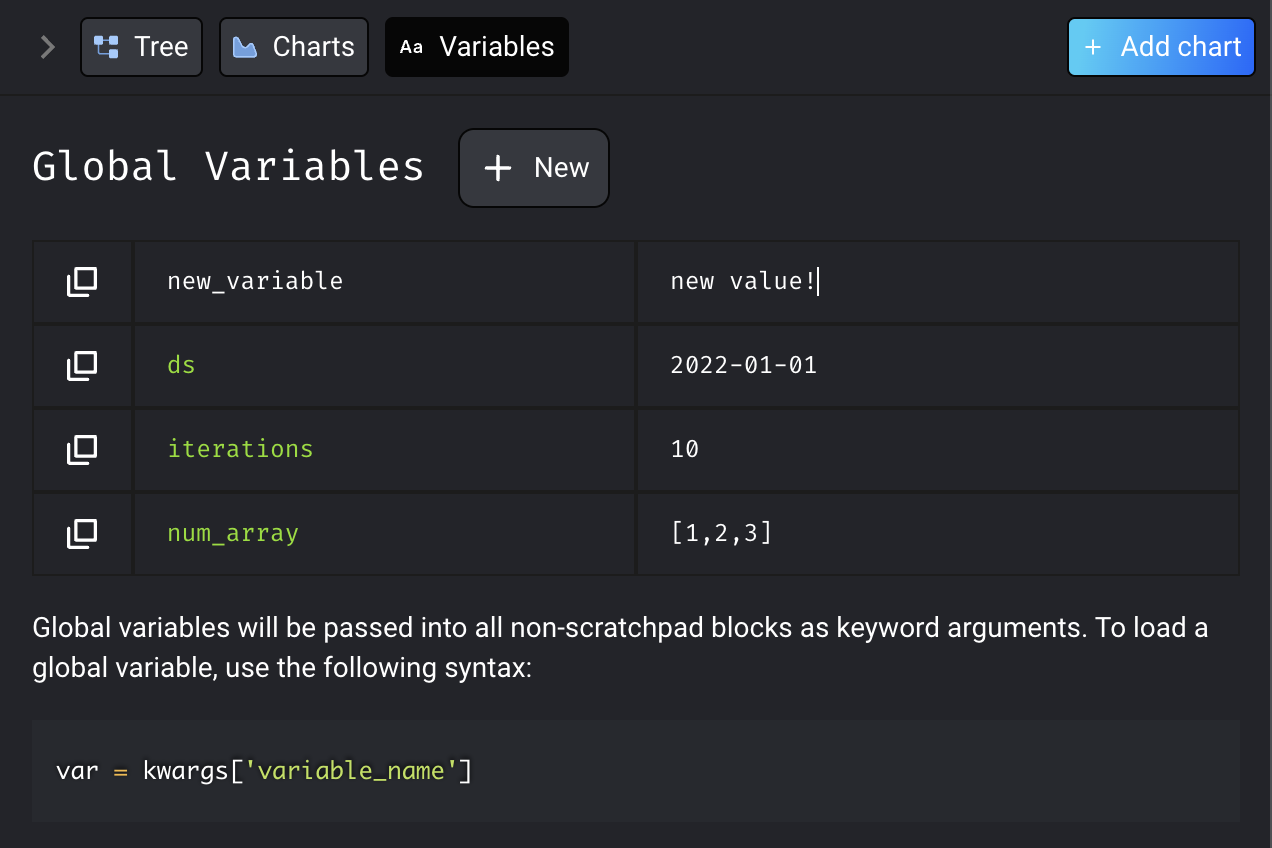
In code
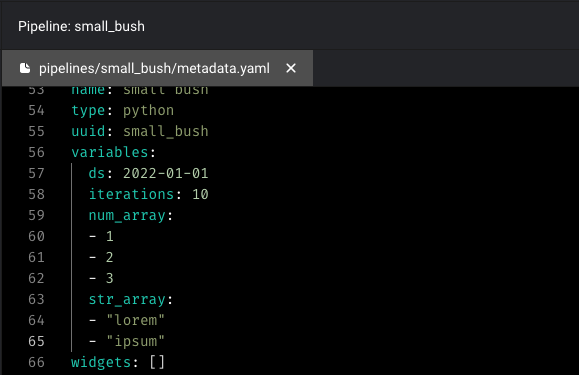
You can also create or edit global variables in code by editing the pipelinemetadata.yaml file.
In Python code
You can also save the variable in Python code. One example usage is to save checkpoint data.Default Runtime Variables
Mage provides some default variables to give context on the pipeline execution.execution_date: A datetime object that the pipeline is executed at.event: If the pipeline is triggered by event, theeventvariable contains the event payload.
Running Pipeline with Runtime Variables
Run from command line
You can execute your pipeline with runtime variables from the command line. First, make sure you installed the package.Run from Python script
If your pipeline is configured to use runtime variables, you can still execute your pipeline outside the code editor. Provide the runtime variables as keyword arguments tomage_ai.run():
Example - Aggregating Daily Logs
A common use of ETL pipelines is to process and analyze daily events. In the case of this example, we will create an ETL pipeline to analyze log messages from a web application. Suppose the following is an example of a log file that our web application produces.| log_date | type | source |
|---|---|---|
| 2022-07-27T20:19:20 | INFO | react-1 |
| 2022-07-27T19:18:45 | WARNING | express-2 |
| 2022-07-27T16:35:28 | DEBUG | react-1 |
| 2022-07-27T10:19:32 | INFO | express-1 |
| 2022-07-27T07:20:26 | ERROR | express-1 |
| 2022-07-27T00:42:37 | ERROR | react-1 |
-
Create a data loader to load all log files modified on a specific date. We
will specify the log folder and the date to load logs from using runtime
variables which are passed to this block via the
**kwargsparameter.Note: This code ignores the edge case of a log file that spills over between days. Since the modification date is used instead of the creation date, a log file that is modified between days will only be considered in the latter day. -
Calculate the distribution of log types over this date
The result of this transformer is a new data frame that looks like below:
DEBUG ERROR INFO WARNING 2022-07-28 816 765 828 871
mage_ai.run(), providing the current date and log folder as keyword arguments:
Example - Model Rockets
Consider the following sample data tracking the launch angle (in degrees) and vertical velocity (in meters per second) of model rocket tests:| launch_id | angle | vertical_velocity |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 28.4 | 61.34 |
| 2 | 14.4 | 32.03 |
| 3 | 61.4 | 113.19 |
| 4 | 44.2 | 89.96 |
| 5 | 39.5 | 82.00 |
| 6 | 79.3 | 126.73 |
| 7 | 74.9 | 124.51 |
| 8 | 38.1 | 79.6 |
pi runtime variable (passed in through
**kwargs) to convert the degrees column of some input data frame to a radians.
This allows us to control the precision with which we want to store pi.
conversion_factor (again passed in through **kwargs), the vertical velocity
in kilometers per hour can be computed:
mage_ai.run(). Specify values for runtime variables as keyword arguments to
this function:

