Mage server
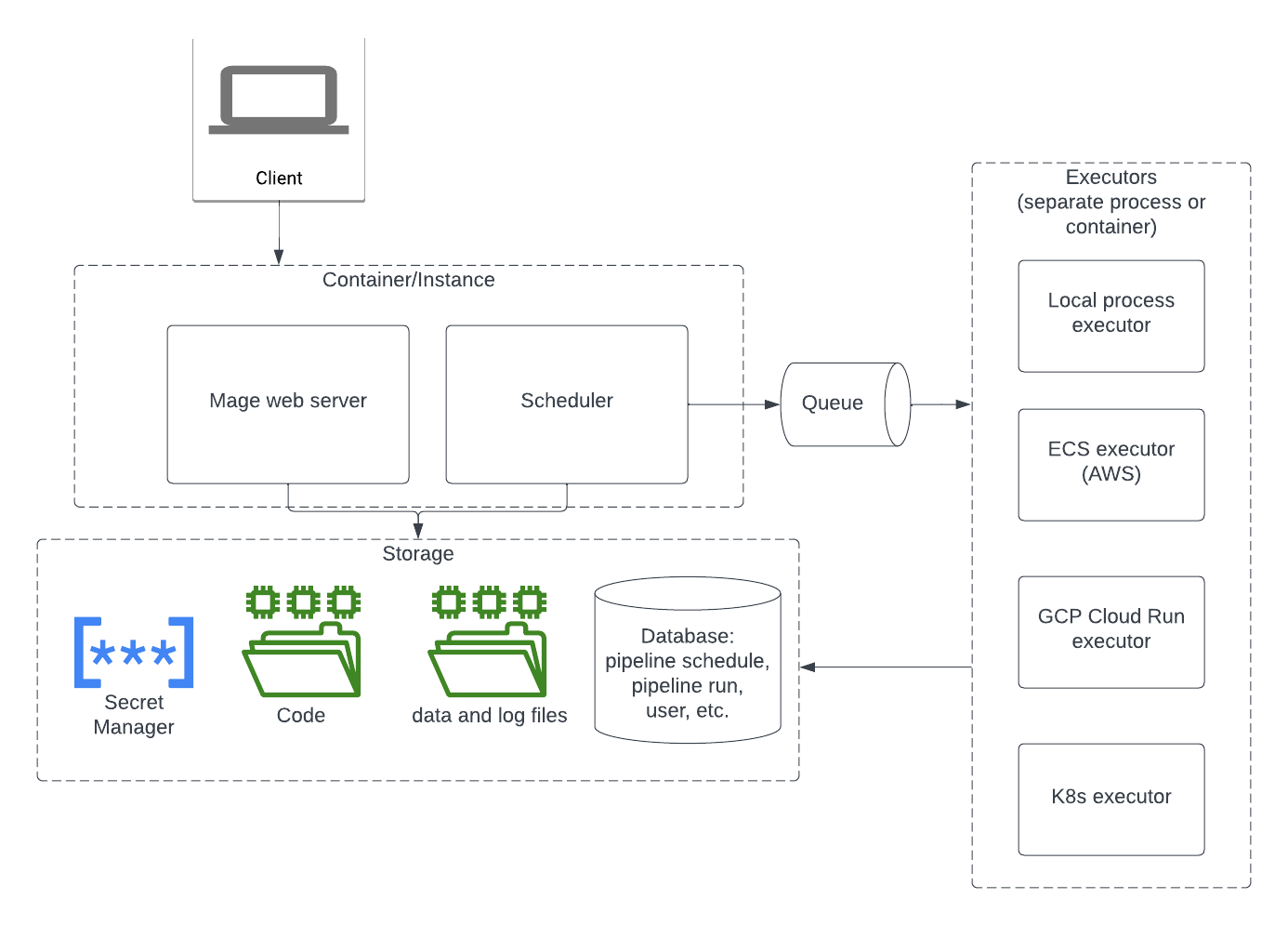
Mage server runs in an instance or container. Here are the responsibilities of the Mage server.- Handle all the API requests.
- Interact with the storage to read and write data.
- Run the websocket server to handle websocket requests.
- Execute the pipeline code in the kernel.
- Handle user authentication.
Storage
In the storage layer, Mage stores the following data:- Code files: Mage stores code files on the local disk. You can use git to sync the code between your local disk and remote the git repository. If you deploy Mage in containers, you can mount an Network File System share in your container to persist the code and data on your disk.
- Data and log files: By default, Mage stores data and log files on the local disk. You can also configure it to store logs in an external storage.
- Pipeline Trigger, Pipeline Run, User data, etc.: Orchestration related objects and authentication related objects are stored in a database. By default, Mage uses a local SQLite database. In a production environment, You can configure Mage to use a Postgres database.
- Secrets: Mage supports storing secrests in the database. It’s also recommended to use an external Secret Manager to store secrets.
Executors
Mage supports different types of executors to execute jobs:- Local process executor
- ECS executor (AWS)
- GCP Cloud Run executor
- Kubernetes executor
Scale web server and schedulers
By default, Mage runs the web server and scheduler in the same container. Mage supports horizontally scaling by separating the web server and scheduler, and run multiple replicas of web servers and schedulers. To separate the web server and scheduler, you can override the container command with the commands below:- Run scheduler only
- Run web server only
REDIS_URL environment variable in your container. The Redis storage is used to coordinate the job scheduling between multiple containers to resolve race conditions. Here is an example Redis URL format: redis://redis:6379/0
