values.yaml file for the
Helm chart:
Permissions
Once your cluster and initial deployment is created, you will also need to give your Kubernetes service account some permissions in order to create the necessary resources. You can run the folliwngkubectl command to create the ClusterRole required for
managing the Kubernetes resources.
default:
Configuration
When creating a new Kubernetes workspace, you can configure the following Kubernetes settings: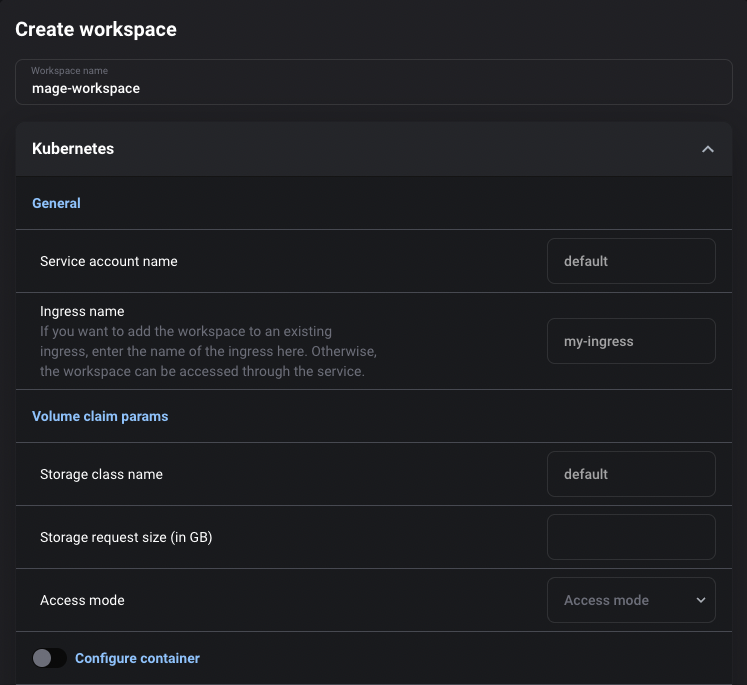
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Workspace name | Name of workspace. This name will be used to create all resources for the workspace. |
| Service account name | Kubernetes service account to use to create the resources. Defaults to current pod’s service account name. |
| Ingress name | Name of ingress to add the new workspace to. See more information about the ingress set up below. |
| Storage class name | Name of storage class to provision storage from for the stateful set. Defaults to current pvc’s storage class name. |
| Storage request size | Amount of storage to provision for the persistent volume claim (in GB). Defaults to current pvc’s storage request. |
| Access mode | Access mode for persistent volume claim. More info in Kubernetes docs. Defaults to current pvc’s access mode. |
| Configure container | Customize the configuration for the container. Configuration options |
Lifecycle management
Available in version
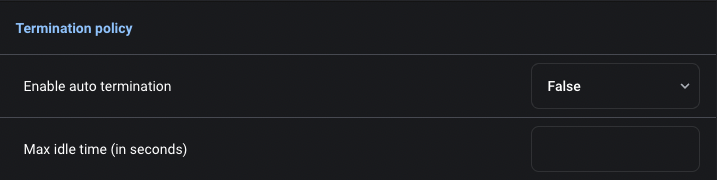
0.9.41 and greater.Auto termination
Auto termination
When the workspace is stopped, Mage will scale down the stateful set to 0, but all the other resources will still exist. The
workspace can be resumed after being stopped through the UI.
Pre start script
Pre start script
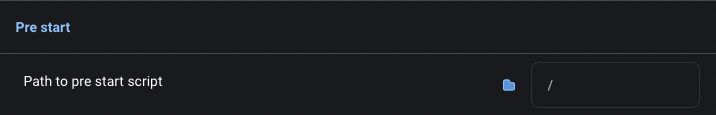
get_custom_configs method that returns a dictionary. The get_custom_configs
method will be passed the container config of the workspace as an argument. Here is an example script:Post start hook
Post start hook
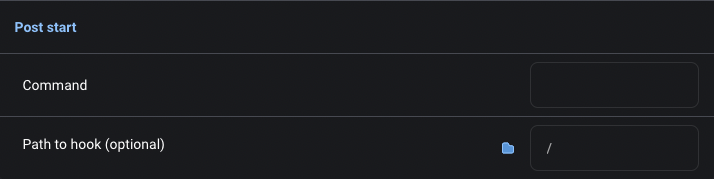
Command: corresponds to the Kuberneteslifecycle.postStart.exec.commandfield. This field is required if you are using a post start hook. This can be a string command or a list.Path to hook: Mage will mount the file specified by this setting to the container. You can reference this fild in your post startcommandto perform more advanced operations. The path of this file will be/app/<file_name>in the container.
Ingress
When an ingress is provided, theMAGE_BASE_PATH environment variable will be set automatically
to the name of the workspace. Thus, the workspace will be accessible at the /<workspace-name> path.
Providing an ingress name will add the workspace to the ingress rules like this:

